Designing AI features that users trust and confidently engage with means paying close attention to the right principles at every stage. Based on the article How to build AI products that users trust: 3 core focus areas to stay user-centric, use this quick checklist to guide your development process and make sure your AI remains user-centred, reliable, and grounded in real-world needs. The questions are grouped into three core focus areas: Familiarity, Fallbacks, and Feedback Loops—each a crucial element for building trustworthy AI products.
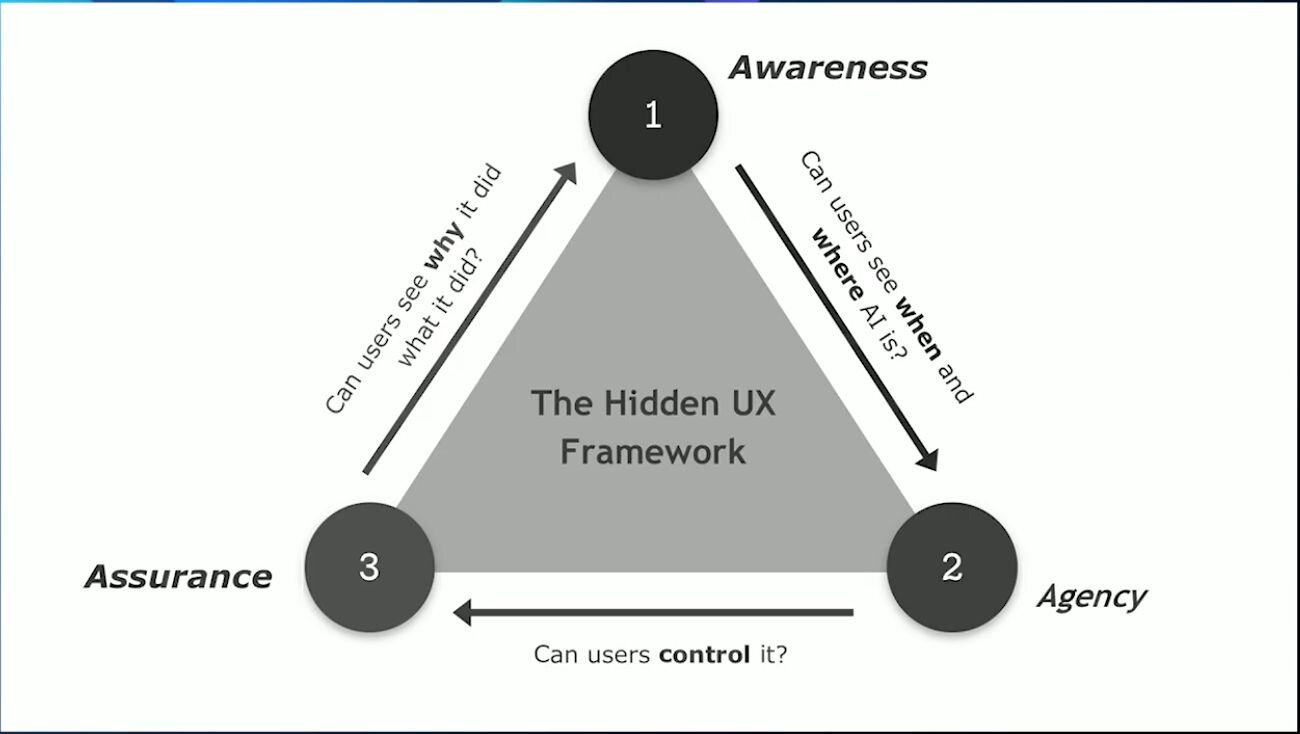
Familiarity: Building trust through transparency
Ask yourself:
- Have you clearly communicated how the AI works, including the data it relies on?
- Does the AI comply with data privacy standards and relevant regulations?
- Is it clear why specific results appear and how they are ranked or determined?
- Have you addressed and mitigated potential biases in the AI, such as gender or racial biases?
- Have you provided straightforward, accessible explanations of the AI’s decision-making process?
- Are the data sources transparent, with links or previews to support the AI’s outputs?
Fallbacks: Safeguards for when things go wrong
Ask yourself:
- Are there default responses for when the AI can’t confidently produce an answer?
- Do users have manual alternatives to solve the problem if the AI doesn’t perform as expected?
- Is human support available for complex or edge-case scenarios?
- Have you built fallback mechanisms, such as faster validation options for time-sensitive features?
- Does the AI perform reliably across different scenarios, with consistent and actionable outputs?
- Can users adjust key settings, such as sensitivity levels, to give them more control?
- Are response times and accuracy optimised, with alternatives in place for when performance drops?
Feedback Loops: Ensuring continuous improvement
Ask yourself:
- Is there an easy way for users to report inaccurate or incomplete AI responses?
- Have you encouraged users to give feedback, making it clear that their input is valued?
- Can users flag specific issues, like poor translations or mismatched entities?
- Are user interactions—inputs, prompts, and outputs—monitored to identify and fix problems?
- Do you have version control for prompts to balance general use cases with edge cases?
- Do you need to implement to track and refine AI interactions?
- Are emotional cues—such as hesitation or uncertainty—captured during testing to uncover trust issues?
- Do you address user concerns with empathy to create a more trustworthy and user-centred experience?
Creating successful AI products hinges on a deep understanding of the problem you’re solving and the underlying needs and concerns of your users. This approach should guide every stage of development, from crafting prompts to building the infrastructure that supports functionality, and ultimately to designing the user-facing interfaces. By following this checklist, you can stay anchored to the essentials, sidestep common pitfalls, and ensure your AI products are not only effective at addressing real-world problems but also inspire trust and confidence.